Human IDO1
Human IDO1
3dioxygenase; EC 1.13.11.52; IDO; IDO1; IDOIDO-1; INDO; INDOindole 2,3-dioxygenase; Indoleamine 2; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3 dioxygenase; Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase
$198.00 – $3,600.00
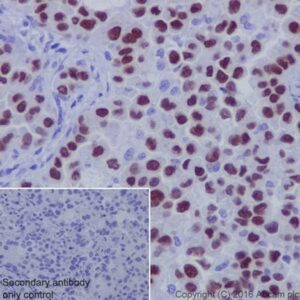
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is a heme-containing intracellular dioxygenase catalyzing the degradation of the essential amino acid L-tryptophan to N formyl kynurenine. IDO is widely expressed in dendritic cells, macrophages, microglia, eosinophils, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and most tumor cells. In immune cells, its expression is mainly induced by cytokines such as IFN gamma, IFN alpha, IFN beta, and IL 10. IDO has an antimicrobial function due to its decreasing the availability of the essential amino acid tryptophan in inflammatory environments. Recent studies have demonstrated that IDO induces immunosuppression during infection, pregnancy, transplantation, autoimmunity, and neoplasia (1-5).

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.